Training Camp 1: Driving Around
Build a Practice Driving Base and make precise and controlled movements.

Lesson Plan
1. Prepare
- Read through the student material in the LEGO® Education SPIKE™ App.
- If you feel it's needed, plan a lesson using the getting started material in the app. This will help familiarize your students with LEGO® Education SPIKE™ Prime.
2. Engage (5 Min.)
- Use the ideas in the Ignite a Discussion section below to engage your students in a discussion related to this lesson.
- Use the video to explain the lesson.
3. Explore (20 Min.)
- Have your students work in pairs to build the Practice Driving Base model.
- Give them some time to use the programming stacks provided to explore the movement of the Driving Base.
- Ask them to change the values and parameters of the blocks and to observe the effects.
4. Explain (5 Min.)
- Facilitate a discussion about the importance of planning each step of their program.
- Explain what pseudocode is and how it can help in their program planning.
5. Elaborate (15 Min.)
- Have your students find a way to move their Driving Base in a square.
- Set up a navigation challenge and encourage your students to test their skills.
- Don't forget to leave some time for cleanup.
6. Evaluate
- Give feedback on each student's performance.
- You can use the assessment rubrics provided to simplify the process.
Ignite a Discussion
Navigating through obstacles on robotics competition fields is a key to success. Engage your students in a discussion by asking them to:
- Describe a field tactic associated with their favorite sport
- List all the movements they think their Driving Base should be able to perform
Have your students watch this video to see what they're about to do.

Building Tips
A Simple Driving Base
Use the simple Driving Base model with no sensors. Remember to use the cable clips.
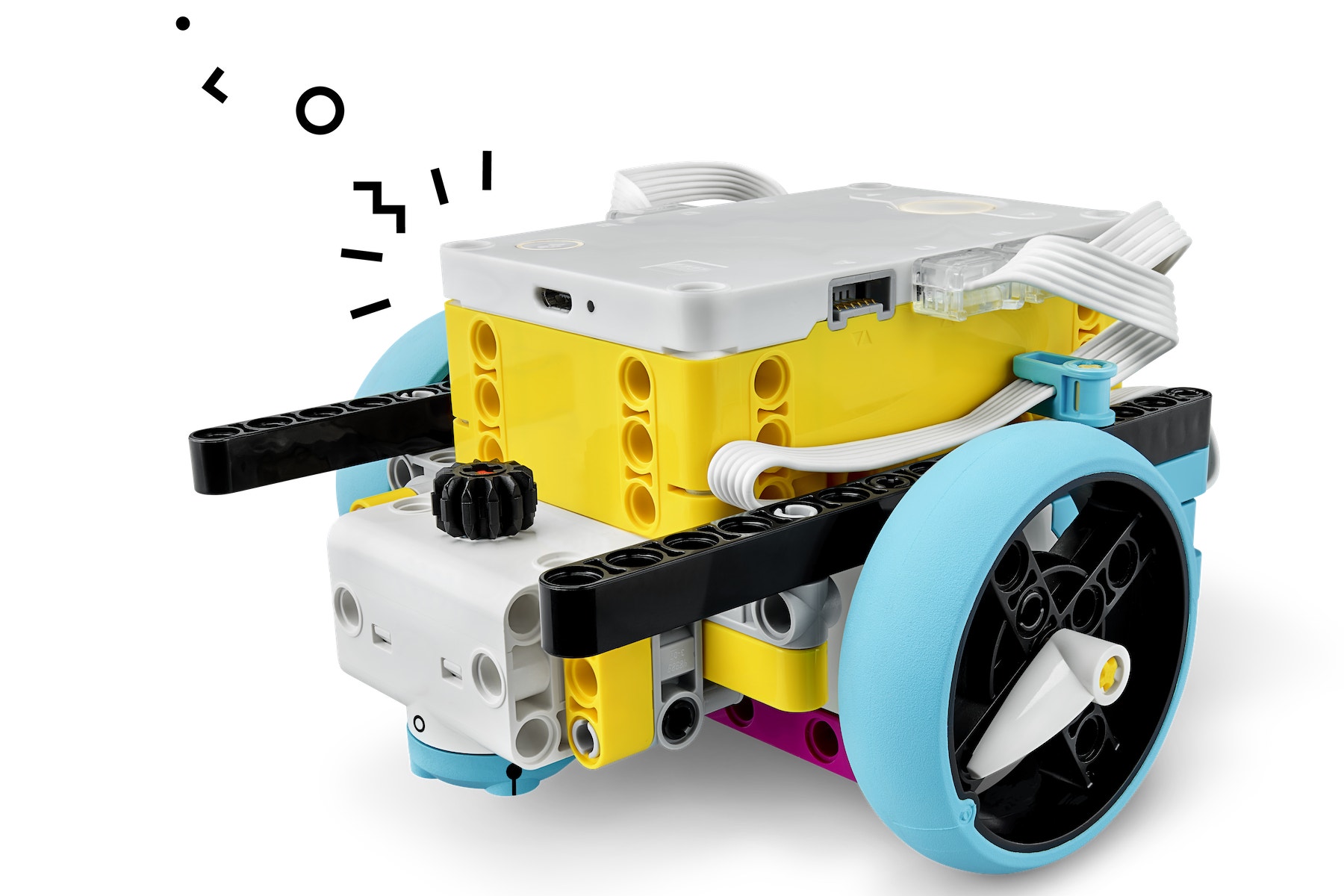
Coding Tips
Main Program

Possible Solution

Other Programs

Differentiation
Simplify this lesson by:
- Spending extra time explaining what is being controlled by each parameter of the program blocks
Take this lesson to the next level by:
- Asking your students to use the Gyro Sensor to program their Driving Base to drive in a square
- Practicing speed and precision on a larger surface, like a competition table
Assessment Opportunities
Teacher Observation Checklist
Create a scale that matches your needs, for example:
- Partially accomplished
- Fully accomplished
- Overachieved
Use the following success criteria to evaluate your students' progress:
- Students can select appropriate blocks for making controlled movements.
- Students can change the parameters of blocks in iterative ways.
- Students can stack appropriate move blocks together to create programs.
Self-Assessment
Have each student choose the brick that they feel best represents their performance.
- Blue: I've made the Driving Base move in different ways.
- Yellow: I've created different programs to move the Driving Base in a square.
- Violet: I've combined different types of motor movements to successfully navigate around obstacles.
Peer-Assessment
Encourage your students to provide feedback to others by:
- Having one student score the performance of another using the colored brick scale above.
- Asking them to present constructive feedback to each other so that they can improve their group's performance during the next lesson.

Language Arts Extension
To incorporate language arts skills development:
- Have your students look for the most precise way of traveling a distance of 2 meters by exploring these options:
▷ Move in seconds
▷ Move in degrees
▷ Move in rotations
▷ Move with sensor - Ask them to create a document explaining in which situation(s) they'd use each option, and why.
Note: This will make for a longer lesson.
Math Extension
To incorporate math skills development:
When calculating distances with the Driving Base:
- Drive forward for one second, one rotation, or a number of degrees. Use this as the basis for estimating the total distance based on the distance traveled.
- Calculate the circumference of the wheel and use this to measure distance traveled (circumference = Pi x diameter, or circumference = Pi x 2 x radius)
Note: This will make for a longer lesson.
Career Links
Students who enjoyed this lesson might be interested in exploring these career pathways:
- Health Science (Medical & Health Careers)
- Information Technology (Game Programming)
Teacher Support
Students will:
- Learn how to execute controlled movements (e.g., straight move, point turn, curved move, turn with sensor, drive in a shape) using a Driving Base
**NGSS
**MS-ETS1-4
Develop a model to generate data for iterative testing and modification of a proposed object, tool, or process such that an optimal design can be achieved.
**CSTA
**2-CS-01 6-8
Recommend improvements to the design of computing devices, based on an analysis of how users interact with the devices.
**Common Core
**CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.7.G.B.4
Know the formulas for the area and circumference of a circle and use them to solve problems; give an informal derivation of the relationship between the circumference and area of a circle.
**CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.6.1
**Write arguments to support claims with clear reasons and relevant evidence.